Overview
What is Dynamic Tiering?
SAP HANA dynamic tiering is a native big data solution for SAP HANA. Dynamic tiering adds smart, disk-based extended storage to your SAP HANA database. Dynamic tiering enhances SAP HANA with large volume, warm data management capability.
SAP HANA dynamic tiering adds the SAP HANA dynamic tiering service (esserver) to your SAP HANA system. You use this service to create the extended store and extended tables. Extended tables behave like all other SAP HANA tables, but their data resides in the disk-based extended store.
Your application automatically determines which tier to save data to: the SAP HANA in-memory store (the hot store), or extended storage (the warm store). When you use SAP HANA to place hot data in SAP HANA in-memory tables, and warm data in extended tables, highest value data remains in memory, and cooler less-valuable data is saved to the extended store. The extended store can reduce the size of your in-memory database.
Features
◉ An optional add-on to the SAP HANA database for managing less frequently accessed warm data.
◉ Its purpose is to extend SAP HANA memory with a disk-centric columnar store (as opposed to the SAP HANA in-memory store).
◉ Dynamic tiering is targeted at SAP HANA database sizes of 512 GB and larger, where large data volumes begin to necessitate a data lifecycle management solution.
◉ SAP HANA dynamic tiering is an integrated component of the SAP HANA database and cannot be operated independently from SAP HANA.
◉ Dynamic tiering is embedded within SAP HANA operational processes, such as standby setup, backup and recovery, and system replication.
◉ Dynamic tiering is also supported by the Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM), an SAP HANA XS-based tool to relocate data from SAP HANA memory to alternate storage locations such as the dynamic tiering extended store, SAP HANA extension nodes, or Hadoop/Vora. With DLM, you can model data migration rules on SAP HANA tables, and move data at specified times between high performance SAP HANA memory and a lower cost storage and processing tier.
Use cases
Dynamic Tiering use cases
Architecture
Dynamic tiering option can be deployed in two ways:
◉ Same host deployment
◉ Dedicated host deployment
You can install SAP HANA and SAP HANA dynamic tiering each on a dedicated server (referred to as a dedicated host deployment) or on the same server (referred to as a same host deployment).
Only one dynamic tiering license is allowed per SAP HANA system. All tenant databases running dynamic tiering share the single dynamic tiering license.
The OS process for the dynamic tiering host is hdbesserver, and the service name is esserver.
Dedicated Host Deployment
Same Host Deployment
Landscape Storage Architecture
SAP HANA and dynamic tiering each support NFS and SAN storage using storage connector APIs.
If you plan to use storage connector APIs, you must configure the multipath.conf and global.ini files before installation.
We used NFS storage in our case which has following requirement:
◉ Both SAP HANA and dynamic tiering hosts have their own dedicated storage.
◉ Both SAP HANA and dynamic tiering hosts, including standby hosts, use storage APIs to access the devices. (Storage API is required only for auto failover mechanism)
◉ Failover nodes mount the storage as part of the failover process.
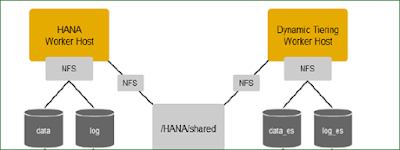
◉ A shared file system (for example, /HANA/shared) is required for installation.
◉ The backup directories for both SAP HANA and dynamic tiering reside on a shared file system, allowing SAP HANA access to the dynamic tiering backup files.
The actual architecture that we followed is as follows:
Dedicated host deployment with /hana/shared/ mounted on both the hosts.
◉ SAP HANA memory <= 2.5TB: size of dynamic tiering storage should not exceed 4x the size of SAP HANA memory.
◉ SAP HANA memory > 2.5TB: size of dynamic tiering storage should not exceed 8x the size of SAP HANA memory.
2086829 – SAP HANA Dynamic Tiering Sizing Ratios
Dynamic Tiering Hardware and Software Requirements
Dynamic tiering is available for:
◉ Intel-based hardware platforms
◉ IBM Power Systems
SAP Note 2365623 – SAP HANA Dynamic Tiering: Supported Operating Systems
2555629 – SAP HANA 2.0 Dynamic Tiering – Hypervisor and Cloud Support
Shared File System Requirements
/hana/shared should be mounted on both the hosts namely HANA host and Dynamic Tiering host which will contain installation files of HANA and Dynamic Tiering service.
On existing HANA DB host we already have two file systems for DATA and LOG:
/hana/data/<SID> àData Volume
/hana/log/<SID>àLog Volume
On Dynamic Tiering Host the following file systems are required which will store ES data and logs:
So after the above setup the actual architecture will appear as follows:
Communication channel and network requirements
There are two types of network used in HANA environment:
1. external(public) network: Channels used for external access to SAP HANA functionality by end-user clients, administration clients, application servers, and for data provisioning via SQL or HTTP
2. internal network: Channels used for SAP HANA internal communication within the database or, in a distributed scenario, for communication between hosts
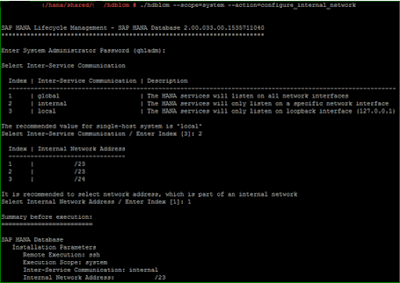
Since we have a distributed scenario here, configuration of internal network becomes mandatory for better system performance and security.
Following parameters is set after configuring internal network between hosts.
global.ini -> [communication] -> listeninterface : .global or .internal
global.ini -> [internal_hostname_resolution] :
mapping rule : internal_ip_address=hostname
The below diagram depicts better understanding of internal networks:
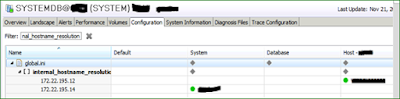
The status after internal network configuration:
Once the listener interface has communication method internal, the two hosts (HANA & DT hosts) can communicate securely and their internal IP addresses reflects in parameter -> internal_hostname_resolution
Installation of Dynamic Tiering Component
Download the relevant compatible Dynamic Tiering software from SAP Marketplace and extract it to a directory.
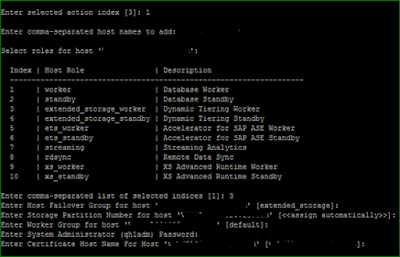
Run hdblcm (with root) with the path of extracted software as parameter and install dynamic tiering component without addition of DT host. (Addition of DT worker host can be performed later)
Installation Process
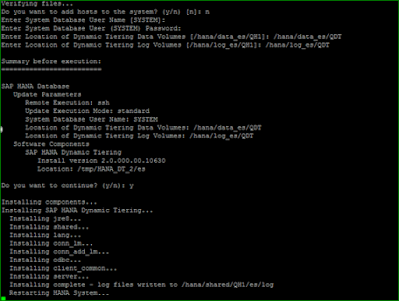
After the dynamic tiering component has been installed on HANA system, start with addition of worker DT host, by running hdblcm from worker DT node.
Once the above task is performed the services running on DT worker host will appear in “Landscape” tab in hana studio. DT service can be checked from OS level by command HDB info
The additional process “hdbesserver” can be seen which confirms that Dynamic-Tiering worker has been successfully installed. In HANA studio this process corresponds to “esserver” service.
Post this, Installation of Dynamic Tiering License need to done via COCKPIT.
Provisioning dynamic tiering service to a tenant database
Each tenant requires a dedicated dynamic tiering host. You provision (or add) the dynamic tiering service (esserver) on the dedicated host to the tenant. You can’t provision the same service to multiple tenants. Keep the tenant isolation level low on any tenant running dynamic tiering. Provisioning fails if the isolation level is high. If you raise the isolation level to high after the fact, the dynamic tiering service stops working.
You modify properties in the global.ini file to prepare resources on each tenant database to support SAP HANA dynamic tiering.
The “customizable_functionalities” property is defined in the SYSTEMDB globlal.ini file at the system level. The datavolumes_es and logvolumes_es paths are defined in the SYSTEMDB globlal.ini file at the system level but are applied at the database level. When set, a diamond appears in the database column. The values are visible in the global.ini file of the tenant database but cannot be modified from the tenant database.
This can be achieved by SQL script:
ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION ( ‘global.ini’, ‘SYSTEM’ ) SET( ‘customizable_functionalities’, ‘dynamic_tiering’ ) = ‘true’
Once the esserver service is assigned to a tenant database, the database, not SYSTEMDB, owns the service.
Assignment of esserver is done by below sql script:
ALTER DATABASE ADD ‘esserver’ [ AT [ LOCATION] ‘[<dynamic_tiering_hostname>:<port> ]’ ]
The host and port information are that of the SAP HANA dynamic tiering host. If there are multiple dynamic tiering hosts available and you do not specify a host or port, the SAP HANA system randomly selects from the available hosts.
Configuration of Dynamic Tiering
Deploy SAP Data Warehouse Foundation (Data Lifecycle Manager) Delivery Unit on SAP HANA. Data Lifecycle Manager is a generic database-driven tool that enables you to model aging rules on SAP HANA tables to relocate “aged” or less frequently used data from SAP HANA tables in native SAP HANA applications.
Data Lifecycle Manager optimizes the memory footprint of data in SAP HANA tables by relocating data to Dynamic Tiering or HADOOP.
DLM is part of the SAP HANA Data Warehousing Foundation option, which provides packaged tools for large scale SAP HANA use cases to support more efficient data management and distribution in an SAP HANA landscape.
Install DLM
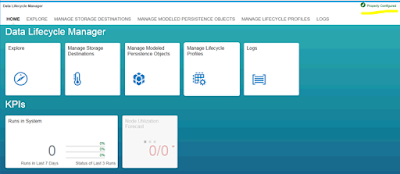
We can install DLM using Hana lifecycle manager as described below:
Select the components and deploy them.
Click on “to be configured”. Copy the commands and deploy in SQL command.
Refresh the page and “To Be Configured” would change to “Properly Configured”
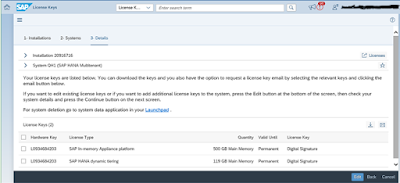
License Management
License is generated on the basis of Main memory in Dynamic Tiering by choosing License type as mentioned below.
Limitations
◉ Scale out of dynamic tiering is not available. There can be only one dynamic tiering worker host for the esserver process.
◉ The BACKINT interface is available with SAP HANA dynamic tiering.
◉ The delta backup mechanism is not available with SAP HANA dynamic tiering.
◉ Storage snapshots cannot be prepared in SAP HANA systems in which dynamic tiering is enabled
◉ Persistence encryption of the SAP HANA system is not available when dynamic tiering is installed.
◉ System replication cannot be used in SAP HANA systems in which dynamic tiering is enabled.





















No comments:
Post a Comment