I am writing this blog to show training with APL using python package hana_ml. With APL, you can automate preprocessing to some extent.
Environment
Environment is as below.
◉ Python: 3.7.14(Google Colaboratory)
◉ HANA: Cloud Edition 2022.16
Python packages and their versions.
◉ hana_ml: 2.14.22091801
◉ pandas: 1.3.5
◉ scikit-learn: 1.0.2
As for HANA Cloud, I activated scriptserver and created my users. Though I don’t recognize other special configurations, I may miss something since our HANA Cloud was created long time before.
I didn’t use HDI here to make environment simple.
Python Script
1. Install Python packages
Install python package hana_ml, which is not pre-installed on Google Colaboratory.
As for pandas and scikit-learn, I used pre-installed ones.
!pip install hana_ml
2. Import modules
Import python package modules.
import pprint
from hana_ml.algorithms.apl.apl_base import get_apl_version
from hana_ml.algorithms.apl.gradient_boosting_classification \
import GradientBoostingBinaryClassifier
from hana_ml.algorithms.pal.partition import train_test_val_split
from hana_ml.dataframe import ConnectionContext, create_dataframe_from_pandas
from hana_ml.model_storage import ModelStorage
from hana_ml.visualizers.unified_report import UnifiedReport
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
3. Connect to HANA Cloud
Connect to HANA Cloud and check its version.
ConnectionContext class is for connection to HANA. You can check the APL version with get_apl_version function.
HOST = '<HANA HOST NAME>'
SCHEMA = USER = '<USER NAME>'
PASS = '<PASSWORD>'
conn = ConnectionContext(address=HOST, port=443, user=USER,
password=PASS, schema=SCHEMA)
print(conn.hana_version())
# APL.Version.ServicePack is APL
print(get_apl_version(conn))
4.00.000.00.1660640318 (fa/CE2022.16)
name value
0 APL.Version.Major 4
1 APL.Version.Minor 400
2 APL.Version.ServicePack 2209
3 APL.Version.Patch 1
4 APL.Info Automated Predictive Library
5 AFLSDK.Version.Major 2
6 AFLSDK.Version.Minor 16
7 AFLSDK.Version.Patch 0
8 AFLSDK.Info 2.16.0
9 AFLSDK.Build.Version.Major 2
10 AFLSDK.Build.Version.Minor 13
11 AFLSDK.Build.Version.Patch 0
12 AutomatedAnalytics.Version.Major 10
13 AutomatedAnalytics.Version.Minor 2209
14 AutomatedAnalytics.Version.ServicePack 1
15 AutomatedAnalytics.Version.Patch 0
16 AutomatedAnalytics.Info Automated Analytics
17 HDB.Version 4.00.000.00.1660640318
18 SQLAutoContent.Date 2022-04-19
19 SQLAutoContent.Version 4.400.2209.1
20 SQLAutoContent.Caption Automated Predictive SQL Library for Hana Cloud
4. Create test data
Create test data using scikit-learn.
There are 3 features and 1 target variable.
def make_df():
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000,
n_features=3, n_redundant=0)
df = pd.DataFrame(X, columns=['X1', 'X2', 'X3'])
df['CLASS'] = y
return df
df = make_df()
print(df)
df.info()
Here is dataframe overview.
X1 X2 X3 CLASS
0 0.964229 1.995667 0.244143 1
1 -1.358062 -0.254956 0.502890 0
2 1.732057 0.261251 -2.214177 1
3 -1.519878 1.023710 -0.262691 0
4 4.020262 1.381454 -1.582143 1
.. ... ... ... ...
995 -0.247950 0.500666 -0.219276 1
996 -1.918810 0.183850 -1.448264 0
997 -0.605083 -0.491902 1.889303 0
998 -0.742692 0.265878 -0.792163 0
999 2.189423 0.742682 -2.075825 1
[1000 rows x 4 columns]
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 1000 entries, 0 to 999
Data columns (total 4 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 X1 1000 non-null float64
1 X2 1000 non-null float64
2 X3 1000 non-null float64
3 CLASS 1000 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(1)
memory usage: 31.4 KB
5. define table and upload data
Define HANA Table and upload data using function “create_dataframe_from_pandas”.
The function is very useful, since it automatically define table and upload at the same time. Please check options for further detail.
TRAIN_TABLE = 'PAL_TRAIN'
dfh = create_dataframe_from_pandas(conn, df, TRAIN_TABLE,
schema=SCHEMA,
force=True, # True: truncate and insert
replace=True) # True: Null is replaced by 0
6. Split data into train and test dataset
Split dataset using function “train_test_val_split”. The function needs key columns, so I added key column using function “add_id”.
train, test, _ = train_test_val_split(dfh.add_id(),
testing_percentage=0.2,
validation_percentage=0)
print(f'Train shape: {train.shape}, Test Shape: {test.shape}')
Train shape: [8000, 5], Test Shape: [2000, 5]
7. Training
Train with random forest by using class “GradientBoostingClassifier”. Please make sure class AutoClassifier is deprecated.
model = GradientBoostingBinaryClassifier()
model.fit(train, label='CLASS', key='ID', build_report=True)
8. Training result
8.1. Unified Report
Model report shows with the below code. Please see another article “Python hana_ml: PAL Classification Training(UnifiedClassification)” for the report content, which is basically same.
model.generate_notebook_iframe_report()
model.generate_html_report('apl')
8.2. Score
Score function returns mean average accuracy.
# score: mean average accuracy. cannot output other metrics
score = model.score(test)
print(score)
8.3. Summary
get_summary function returns model summary.
model.get_summary().deselect('OID').collect()
8.4. Metrics
get_performance_metrics function returns metrics information.
>> pprint.pprint(model.get_performance_metrics())
{'AUC': 0.991,
'BalancedClassificationRate': 0.964590677634156,
'BalancedErrorRate': 0.03540932236584404,
'BestIteration': 69,
'ClassificationRate': 0.9646017699115044,
'CohenKappa': 0.9291813552683117,
'GINI': 0.4823,
'KS': 0.9195,
'LogLoss': 0.12414480396790141,
'PredictionConfidence': 0.991,
'PredictivePower': 0.982,
'perf_per_iteration': {'LogLoss': [0.617163,
0.554102,
0.499026,
<omit>
0.125448,
0.125588]}}
8.5. Statistical Report
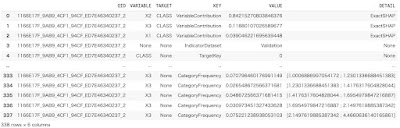
get_debrief_report function returns several type of statistical reports. Please See Statistical Reports in the SAP HANA APL Reference Guide.
reports = ['Statistics_Partition',
'Statistics_Variables',
'Statistics_CategoryFrequencies',
'Statistics_GroupFrequencies',
'Statistics_ContinuousVariables',
'ClassificationRegression_VariablesCorrelation',
'ClassificationRegression_VariablesContribution',
'ClassificationRegression_VariablesExclusion',
'Classification_BinaryClass_ConfusionMatrix']
for report in reports:
print('\n'+report)
display(model.get_debrief_report(report).deselect('Oid').head(3).collect())
8.6. Indicators
get_indicators function returns all indicators with unified format.
model.get_indicators().collect()
8.7. Model info
get_model_info function returns several type of reports.
for model_info in model.get_model_info():
print('\n', model_info.source_table['TABLE_NAME'])
display(model_info.deselect('OID').head(3).collect())
9. Predict
You can predict with function predict.
>> model.set_params(extra_applyout_settings={'APL/ApplyExtraMode': 'Individual Contributions'})
>> apply_out = model.predict(test)
>> print(apply_out.head(3).collect())
ID TRUE_LABEL PREDICTED gb_score_CLASS gb_contrib_X1 gb_contrib_X2 gb_contrib_X3 gb_contrib_constant_bias
0 12 0 0 2.592326 -0.222146 3.193908 -0.383197 0.003759
1 13 1 1 -4.876161 0.141867 -4.717393 -0.304394 0.003759
2 19 1 1 -4.074210 0.433828 -4.438335 -0.073464 0.003759
10. Save model
Just save model with class “ModelStorage” and function “save_model”.
ms = ModelStorage(conn)
# ms.clean_up()
model.name = 'My classification model name'
ms.save_model(model, if_exists='replace')
You can see the saved model.
# display(ms.list_models())
pprint.pprint(ms.list_models().to_dict())
{'CLASS': {0: 'hana_ml.algorithms.apl.gradient_boosting_classification.GradientBoostingBinaryClassifier'},
'JSON': {0: '{"model_attributes": {"name": "My classification model name", '
'"version": 1, "log_level": 8, "model_format": "bin", "language": '
'"en", "label": "CLASS", "auto_metric_sampling": false}, '
'"fit_params": {}, "artifacts": {"schema": "I348221", '
'"model_tables": ["HANAML_APL_MODELS_DEFAULT"], "library": '
'"APL"}, "pal_meta": {}}'},
'LIBRARY': {0: 'APL'},
'MODEL_REPORT': {0: None},
'MODEL_STORAGE_VER': {0: 1},
'NAME': {0: 'My classification model name'},
'SCHEDULE': {0: '{"schedule": {"status": "inactive", "schedule_time": "every '
'1 hours", "pid": null, "client": null, "connection": '
'{"userkey": "your_userkey", "encrypt": "false", '
'"sslValidateCertificate": "true"}, "hana_ml_obj": '
'"hana_ml.algorithms.pal.xx", "init_params": {}, '
'"fit_params": {}, "training_dataset_select_statement": '
'"SELECT * FROM YOUR_TABLE"}}'},
'STORAGE_TYPE': {0: 'default'},
'TIMESTAMP': {0: Timestamp('2022-09-21 08:57:33')},
'VERSION': {0: 1}}
11. Close connection
Last but not least, close the connection.
conn.close()



No comments:
Post a Comment