In the previous sessions we learnt
This is the perfect time to revisit the Modeler perspective and check its different components.
To open a perspective, go to Window -> Open Perspective.
Quick Tour: Modeler Perspective:
- SAP HANA Studio has different perspectives like Modeler, Administration, Debug etc. (Section 3.4)
- We use Modeler perspective to create Attribute view, Analytic View and Calculation view.
This is the perfect time to revisit the Modeler perspective and check its different components.
To open a perspective, go to Window -> Open Perspective.
Quick Tour: Modeler Perspective:
The perspective contains the following main areas:
SAP HANA Systems view:
A view of the database objects, that is, those objects you create from the Modeler perspective.
Quick Launch area:
A collection of shortcuts for performing the most common modeling tasks. If you close the Quick Launch tab, you can reopen it by selecting Help -> Quick Launch.
Properties view:
A view that consists of all the object properties.
Job Log view:
A view that displays information related to requests entered for a job such as, validation, activation, and so on.
Where-Used view:
A view that list down all the objects where the selected object has been used.
SAP HANA Systems View:
The Systems view is divided into the following main sections:
Security
Contains the roles and users defined for this system.
Catalog
Contains the database objects that have been activated, for example, from design-time objects or from SQL DDL statements. The objects are divided into schemas, which is a way to organize activated database objects.
Provisioning
Contains administrator tools for configuring smart data access, data provisioning, and emote data sources
Content
Contains design-time database objects, both those that have been activated and those not activated
Modeling View Editor Components:
In the Modeler perspective, you use the view editor to work with the modeling views. This editor is also known as One View editor. The editor is common across the three types of views. However the editor components vary based on the view types as follows:
Modeling View Editor for Attribute View:
The Scenario panel of the editor consists of the following default nodes:
Data Foundation : represents the tables used for defining the view.
Semantics represents the output structure of the view, that is, the dimension.
The Details panel consists of the following views:
Properties: displays basic view properties
Column:
displays view columns that you can define as attributes and key attributes.
Hierarchies:
displays hierarchies that you create for arranging the view attributes hierarchically.
Modeling View Editor for Analytic View:
The Scenario panel of the editor consists of the following default nodes:
Data Foundation: represents the tables used for defining the fact table and related tables of the view.
Logical Join: represents the relationship between the selected table fields (fact table) and attribute views that is, used to create the star schema.
Semantics: represents the output structure of the view.
The Details panel consists of the following views:
Properties: displays basic view properties.
Column: contains analytic view local columns that you can define as attributes and measures, and shared attributes from the underlying attribute views. You can define several display folders and assign the measures to these display folders for grouping the related measures.
Hierarchies: contains hierarchies from the underlying attribute views.
Variables/Input Parameters: contains variables and input parameters used to filter attribute data and to obtain a desired functionality when the view is executed based on the value provided at runtime.
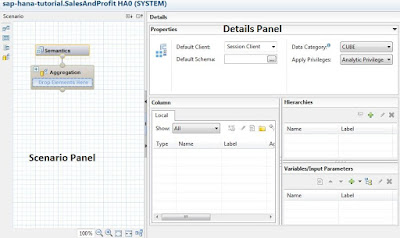
Modeling View Editor for Graphical Calculation View:
The Scenario panel of the editor consists of the following default nodes:
Aggregation / Projection node: based on your setting for the property “Data Category” to true or false, these default nodes appear. If the property is set to true, the default node is aggregation node. If the property is set to false, the default node is projection node.
Note -You can change the default node in the Scenario panel as required; for example, projection node to aggregation node using the context menu option “Switch to Aggregation”.
Semantics: represents the output structure of the view.
The Details panel consists of the following views:
Properties: displays basic view properties
Column: contains analytic view local columns that you can define as attributes and measures. You can define several display folders and assign the measures to these display folders for grouping the related measures.
Hierarchies: contains hierarchies from the underlying attribute views.
Variables/Input Parameters: contains variables and input parameters used to filter attribute data and to obtain a desired functionality when the view is executed based on the value provided at runtime.
Modeling View Editor for Scripted Calculation View:
The Scenario panel of the editor consists of the following default nodes:
Script_View: represents the script, that is, a series of SQL statements defining calculation view logic.
Semantics: represents the output structure of the view.
The Details panel consists of the following views:
Properties: displays basic view properties.
Column: contains analytic view local columns that you can define as attributes and measures. You can define several display folders and assign the measures to these display folders for grouping the related measures.
Hierarchies: contains hierarchies from the underlying attribute views.
Variables/Input Parameters: contains variables and input parameters used to filter attribute data and to obtain a desired functionality when the view is executed based on the value provided at runtime.


No comments:
Post a Comment